Uniform Distribution
Also known as a rectangular distribution. The uniform distribution lies between two values on the x-axis. The total area is equal to 1.0 or 100% within the rectangle. There are not any peaks, valleys, or slopes.
A regular (and fair) six-sided die is a good example because each of the six sides has an equal probability of occurring. Each side has a 1/6 chance of occurring each time. There is replacement each roll.
The same would apply for a roulette wheel...assuming the wheel is fair. Ignoring the green numbers of 0 and 00 depending on whether the game is American or European, there are 36 numbers. Each of the numbers has the same 1/36 chance of occurring. Again, there is replacement after each spin.
Assume "k" equals the number of different values that can occur and each value has the same chance and that chance remains constant, then P = 1/k.
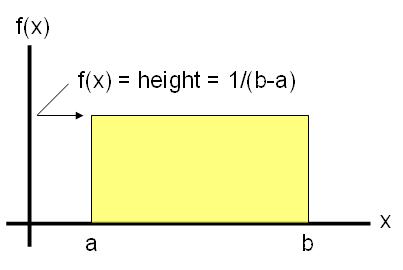

Example using the Uniform Distribution

Search active job openings related to Six Sigma
Site Membership
Click for a Password
to access entire site
Six Sigma
Templates & Calculators
Six Sigma Modules
The following are available
Click Here
Green Belt Program (1,000+ Slides)
Basic Statistics
Cost of Quality
SPC
Process Mapping
Capability Studies
MSA
Cause & Effect Matrix
FMEA
Multivariate Analysis
Central Limit Theorem
Confidence Intervals
Hypothesis Testing
T Tests
1-Way ANOVA
Chi-Square
Correlation and Regression
Control Plan
Kaizen
MTBF and MTTR
Project Pitfalls
Error Proofing
Effective Meetings
OEE
Takt Time
Line Balancing
Practice Exam
... and more


